Change In Momentum Formula
Change In Momentum Formula - This is true since momentum change mass velocity change There are also a few observations that can be made that relate to the qualitative nature of the impulse momentum change theorem An examination of rows 1 and 2 show that force and time are inversely proportional for the same mass and velocity change a tenfold increase in the Both impulse and change in momentum are important physics concepts and have important implications in multiple areas such as analyzing collisions predicting crash injuries and even helping to analyze rockets and space travel If you check out the units used in either F t or in m v you get two new unit combinations Ns and kg m s or kg ms
Change In Momentum Formula

Change In Momentum Formula
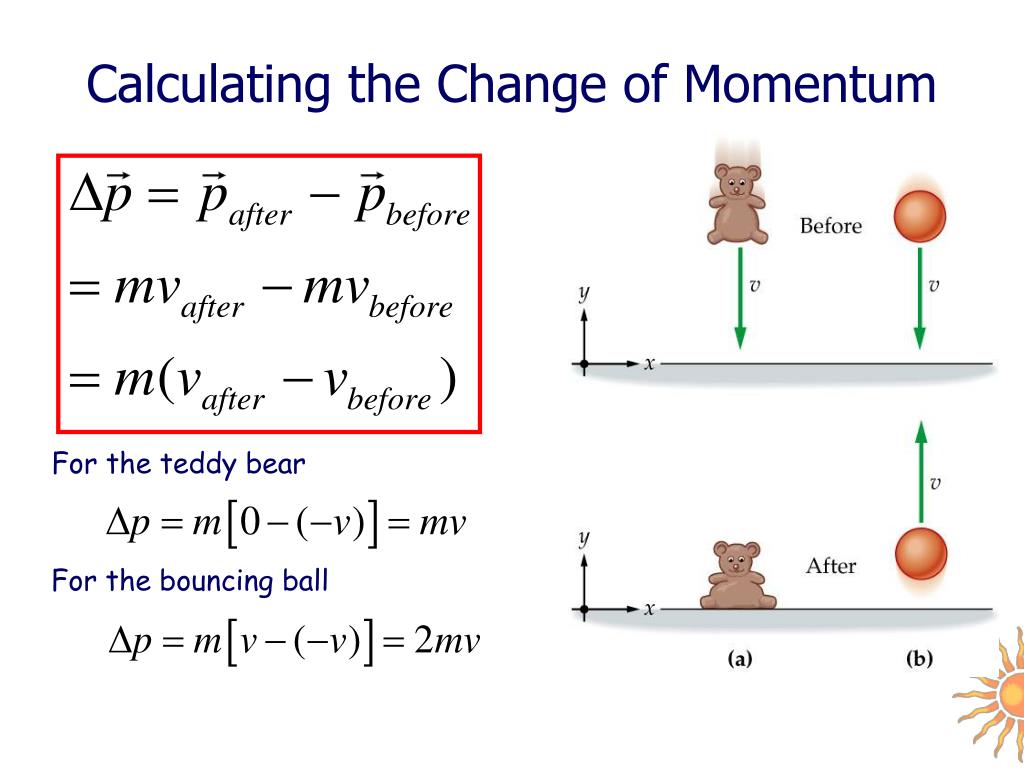
To determine the change in momentum, substitute the values for mass and the initial and final velocities into the equation above. Δ p = m ( v f − v i ) = ( 0 .057 kg ) ( 58 m/s – 0 m/s ) = 3 .306 kg·m/s ≈ 3 .3 kg·m/s Δ p = m ( v f − v i ) = ( 0 .057 kg ) ( 58 m/s – 0 m/s ) = 3 .306 kg·m/s ≈ 3 .3 kg·m/s What is the change (magnitude and direction) in the linear momentum of the object? Solution:- The below figure shows a 4.88-kg object with a speed of 31.4 m/s strikes a plate of steel at an angle of 42.0° and rebounds at the similar speed with the same angle which is visible geometrically.
Momentum Change In Momentum amp Impulse Foundations Of
How To Find Change In Momentum With Force And Time
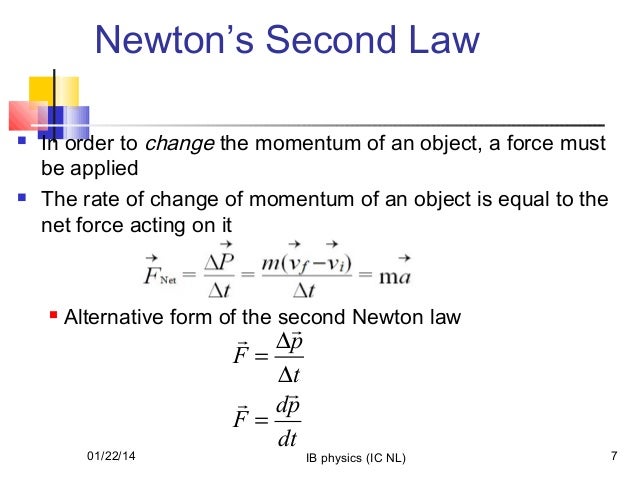
Change In Momentum FormulaΔp = F_net * Δt is the equation to calculate the change in momentum. F_net is the net external force, Δp is change in momentum, and Δt is the time over which a net force acts. Change in momentum is proportional to the net external force and the time over which a net force acts. Hope this helped! Aaron 1 What is the Formula of Change in Momentum The formula to calculate the change in momentum of the object is p m v f v i 2 How do you Calculate Change in Momentum Class 9th If the initial momentum of the object is p 1 mu and the final momentum of object is p 2 mv then the change in momentum is calculated as
Course: Mechanics (Essentials) - Class 11th > Unit 8. Lesson 2: Impulse. Impulse. Calculating linear momentum and change in momentum. Momentum and velocity from force vs. time graphs. Impulse review. Science >. Momentum Definition Formula Science Notes By Teachoo PPT Momentum And Impulse PowerPoint Presentation Free Download ID
Momentum Formula Definition Equation And Examples Toppr
How To Find Change In Momentum Formula
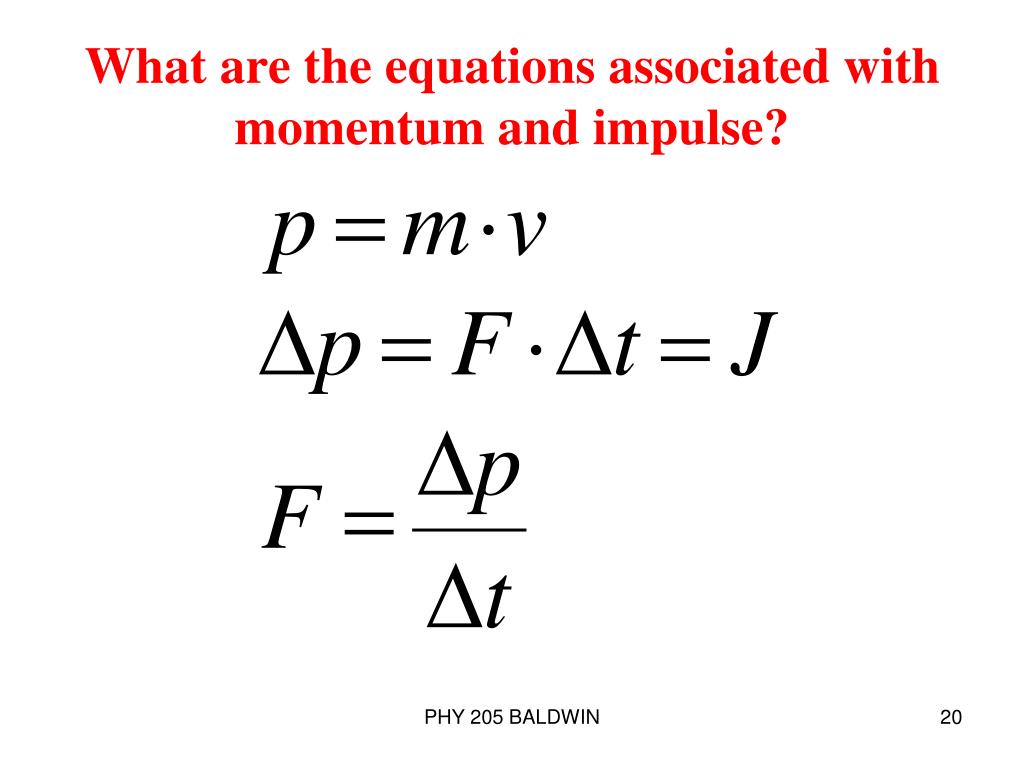
Equations Introduced and Used for this Topic (all equations can be written and solved as both scalar and vector and all equations are generally solved as vectors): Impulse (J) = Ft = ∆pChange in Momentum (∆p) = m∆v. Momentum (p) = mv. ∆p = p f – p i ∆v = v f – v i. Calculating Change In Momentum For An Object In A Constant Mass System
Equations Introduced and Used for this Topic (all equations can be written and solved as both scalar and vector and all equations are generally solved as vectors): Impulse (J) = Ft = ∆pChange in Momentum (∆p) = m∆v. Momentum (p) = mv. ∆p = p f – p i ∆v = v f – v i. Conservation Of Momentum Impulse And Change In Momentum YouTube
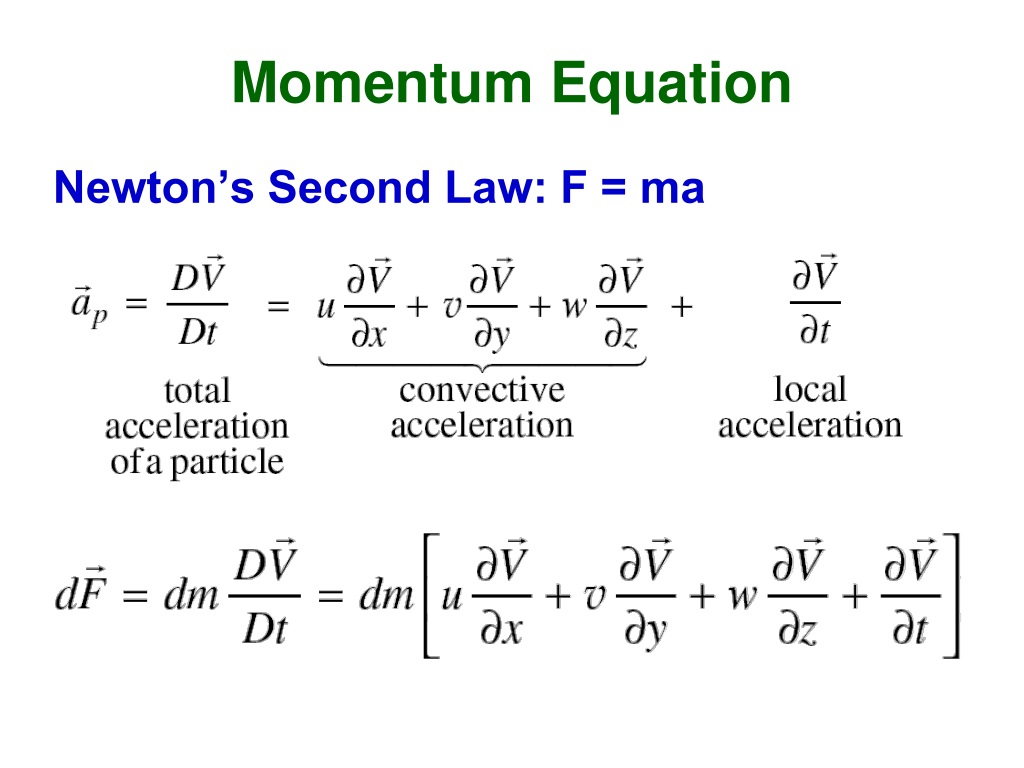
Momentum Equation
Change In Momentum Formula Physics Jungker Malek
PPT Momentum And Momentum Conservation PowerPoint Presentation Free
Linear Momentum
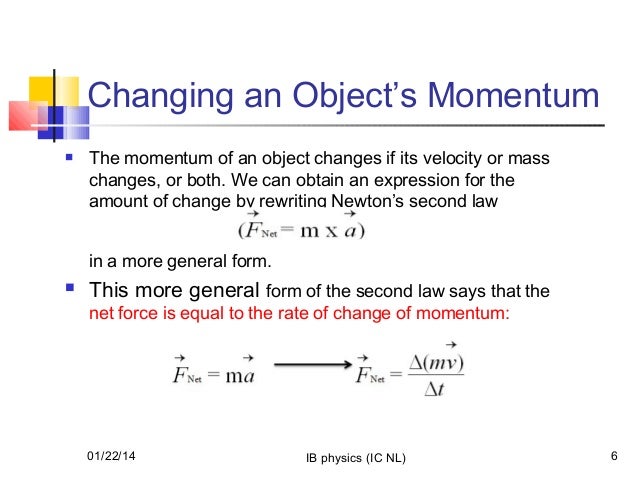
Change In Momentum Formula Units Insight From Leticia
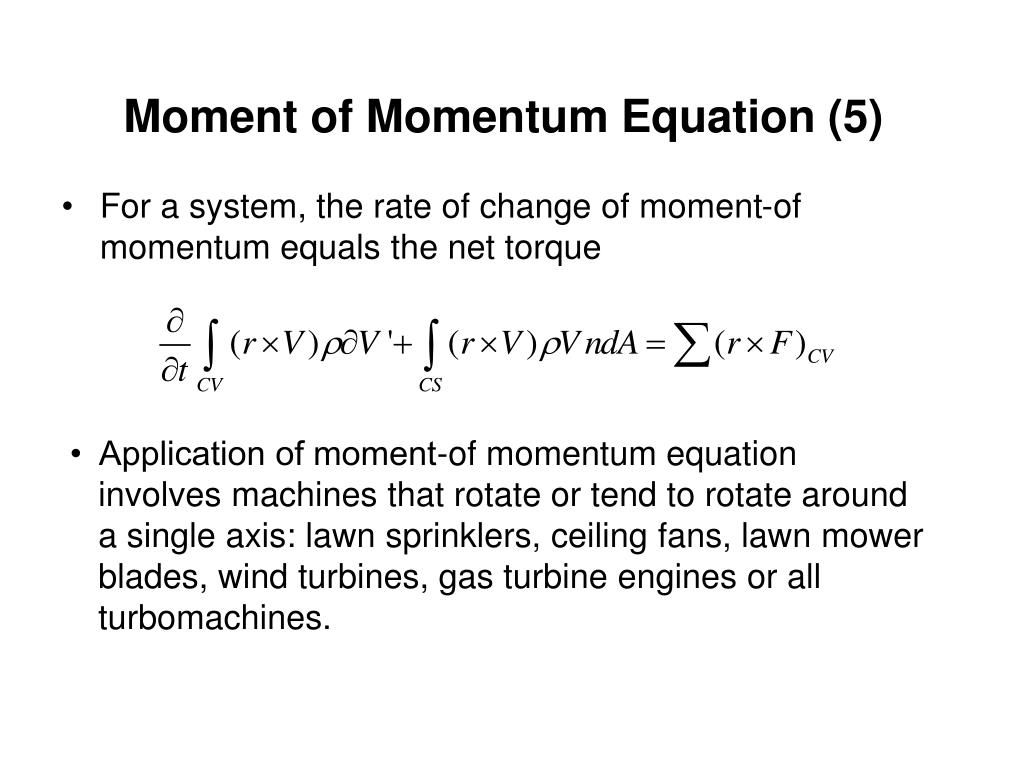
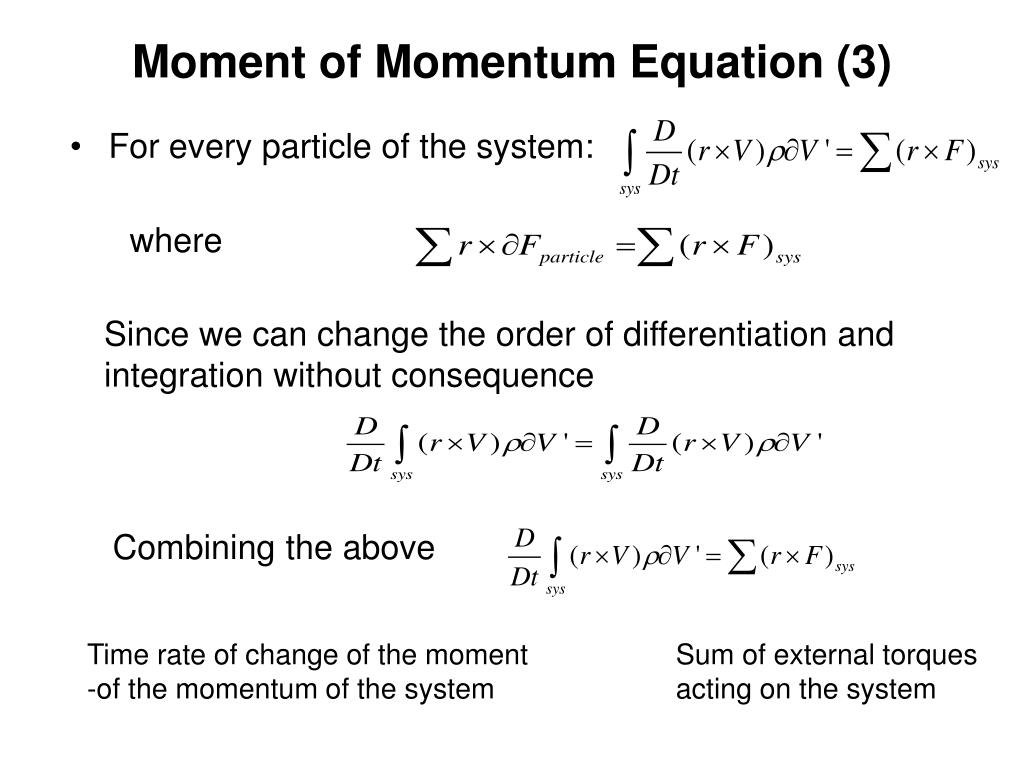
PPT Moment Of Momentum Equation 1 PowerPoint Presentation Free
Force And Momentum Formula
Calculating Change In Momentum For An Object In A Constant Mass System

Question Video Momentum Change Of A Body Due To A Collision Nagwa
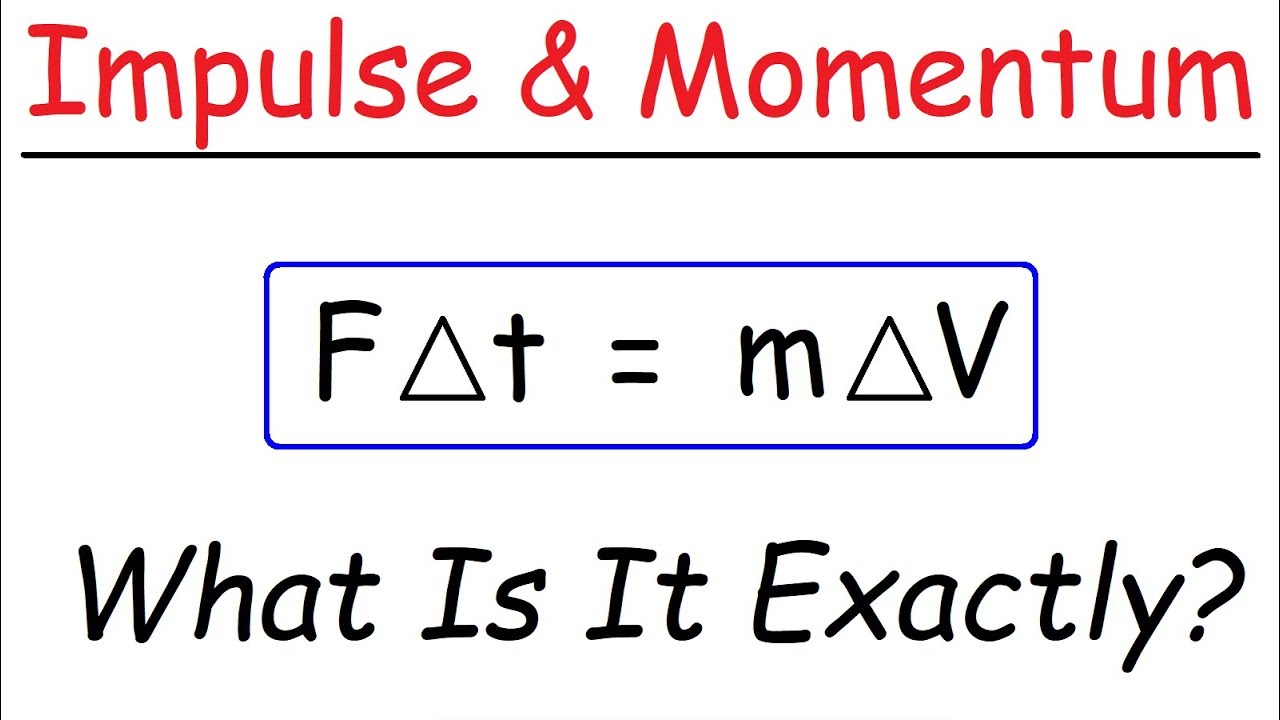
Introduction To Impulse Momentum Physics YouTube