Define Root Mean Square Velocity
Define Root Mean Square Velocity - The root mean square velocity RMS velocity of gas is a square root of the average square velocity Like it it has units of velocity The higher the temperatureof a given gas the greater the RMS velocityof its molecules The heavier the particle the slower it moves and the RMS velocity decreases In the physics of gas molecules the root mean square speed is defined as the square root of the average squared speed The RMS speed of an ideal gas is calculated using the following equation v RMS 3 R T M displaystyle v text RMS sqrt 3RT over M
Define Root Mean Square Velocity

Define Root Mean Square Velocity
The root mean square velocity (RMS velocity) is a way to find a single velocity value for the particles. The average velocity of gas particles is found using the root mean square velocity formula: μ rms = (3RT/M) ½ μ rms = root mean square velocity in m/sec R = ideal gas constant = 8.3145 (kg·m 2 /sec 2 )/K·mol T = absolute. The mean square speed is the second-order raw moment of the speed distribution. The "root mean square speed" v r m s {\displaystyle v_{\mathrm {rms} }} is the square root of the mean square speed, corresponding to the speed of a particle with average kinetic energy , setting b = 1 2 a 2 = m 2 k T {\textstyle b={\frac {1}{2a^{2}}}={\frac {m}{2kT
Root Mean Square Wikipedia
Fine Beautiful Root Mean Square Velocity Derivation Pdf What Is
Define Root Mean Square VelocityRoot mean square velocity is the average velocity of the molecules that make up a gas. This value can be found using the formula: v rms = [3RT/M] 1/2 where v rms = average velocity or root mean square velocity R = ideal gas constant T = absolute temperature M = molar mass The first step is to convert the temperatures to absolute. This study material notes on root mean square velocity defines root mean square velocity and the parameters on which it depends The root mean square velocity of particles in a gas is calculated using the square root of the average velocity squared of the individual molecules in the gas
The inverse proportionality between root-mean-square velocity and the square root of molar mass means that the heavier a molecule is, the slower it moves, which is verified by the examples below. We can compare the rates of effusion or diffusion of a known gas with that of an unknown gas to determine the molar mass of the unknown gas. Root Mean Square Speed YouTube Root Mean Square Speed Chemistry Video Clutch Prep
Maxwell Boltzmann Distribution Wikipedia

The Root Mean Square Velocity A More Reliable Measure Of Average
The root-mean square (RMS) velocity is the value of the square root of the sum of the squares of the stacking velocity values divided by the number of values. The RMS velocity is that of a wave through sub-surface layers of different interval velocities along a. CHEM 101 Calculating Root Mean Square Velocity 2 YouTube
The root-mean square (RMS) velocity is the value of the square root of the sum of the squares of the stacking velocity values divided by the number of values. The RMS velocity is that of a wave through sub-surface layers of different interval velocities along a. Calculate The Root Mean Square Velocity And Kineti Chegg Mean Free Path Mean Free Time Root Mean Square Velocity Formula
Fine Beautiful Root Mean Square Velocity Derivation Pdf What Is
SOLVED Calculate The Root Mean Square Velocity And Kinetic Energy Of CO

The Root Mean Square r m s Velocity Of Hydrogen Molecules At 300 K Is

CHEMISTRY 101 Root Mean Square Velocity Of Gas Molecules YouTube

SOLVED Calculate The Root Mean Square Velocity In M s Of Kr At 23 0
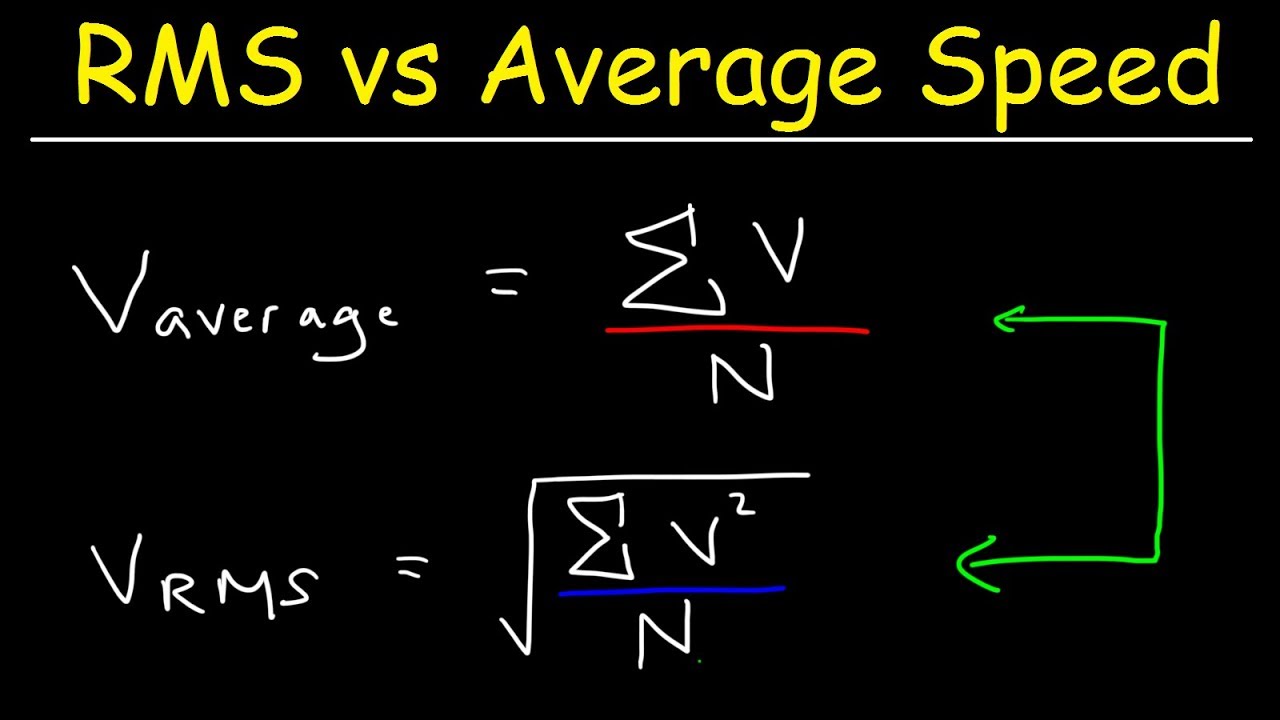
Root Mean Square Speed RMS Vs Average Speed YouTube

What Is Root Mean Square Velocity RMS Speed 6 YouTube

CHEM 101 Calculating Root Mean Square Velocity 2 YouTube

Fine Beautiful Root Mean Square Velocity Derivation Pdf What Is

Root Mean Square Velocity AP Chemistry YouTube

