Second Degree Price Discrimination
Second Degree Price Discrimination - Second degree price discrimination is where a firm sells a good or service at different prices based on quantity For example this may include offers such as buy two get one free or 20 percent off when you buy six Second Degree Price Discrimination Second degree price discrimination involves charging consumers a different price for the amount or quantity consumed Examples include A phone plan that charges a higher rate after a determined amount of minutes are used Reward cards that provide frequent shoppers with a discount on future products
Second Degree Price Discrimination

Second Degree Price Discrimination
Second-degree price discrimination is a pricing strategy in which a business charges different prices to different groups of customers based on specific observable characteristics. Therefore, this technique helps elevate profit margins , attract new customers through different pricing strategies, and ensure customer satisfaction and loyalty. Second-Degree Price Discrimination. Second-degree price discrimination occurs when a company charges a different price for different quantities consumed, such as quantity discounts on bulk.
Price Discrimination Definition Types And Practical Example

Second Degree Price Discrimination
Second Degree Price DiscriminationSecond-degree price discrimination 2 First-degree price discrimination requires: High Income: entry fee $72 and $4 per drink or entry plus 12 drinks for a total charge of $120 Low Income: entry fee $32 and $4 per drink or entry plus 8 drinks for total charge of $64 This will not work high income types get no consumer surplus from the Second degree price discrimination uses this insight in that it charges different prices for different number of units that a consumer buys Examples of second degree price discrimination include quantity discounts when more units are sold at a lower per unit price and block pricing when the consumer pays different price for different
2nd degree: Prices varying by quantity sold such as bulk purchase discounts. Prices varying by time of purchase such as peak-time prices. 3rd degree: Charging different prices to groups of consumers segmented by the coefficient of price elasticity of demand, income, age, sex. Solved 08 Question 2 Points See Page 486 Second degree Chegg 4 Understanding Second degree Price Discrimination Chegg
What Is Price Discrimination And How Does It Work Investopedia

Second Degree Price Discrimination
Second-degree price discrimination can occur when there are different segments of consumers, for example, high demand customers and low demand customers. However, the firm is unable to accurately assign a customer to a segment prior to the sale. Second Degree Price Discrimination Graph And Example
Second-degree price discrimination can occur when there are different segments of consumers, for example, high demand customers and low demand customers. However, the firm is unable to accurately assign a customer to a segment prior to the sale. Second Degree Price Discrimination Graph And Example PPT Second Degree Price Discrimination With Declining AC PowerPoint
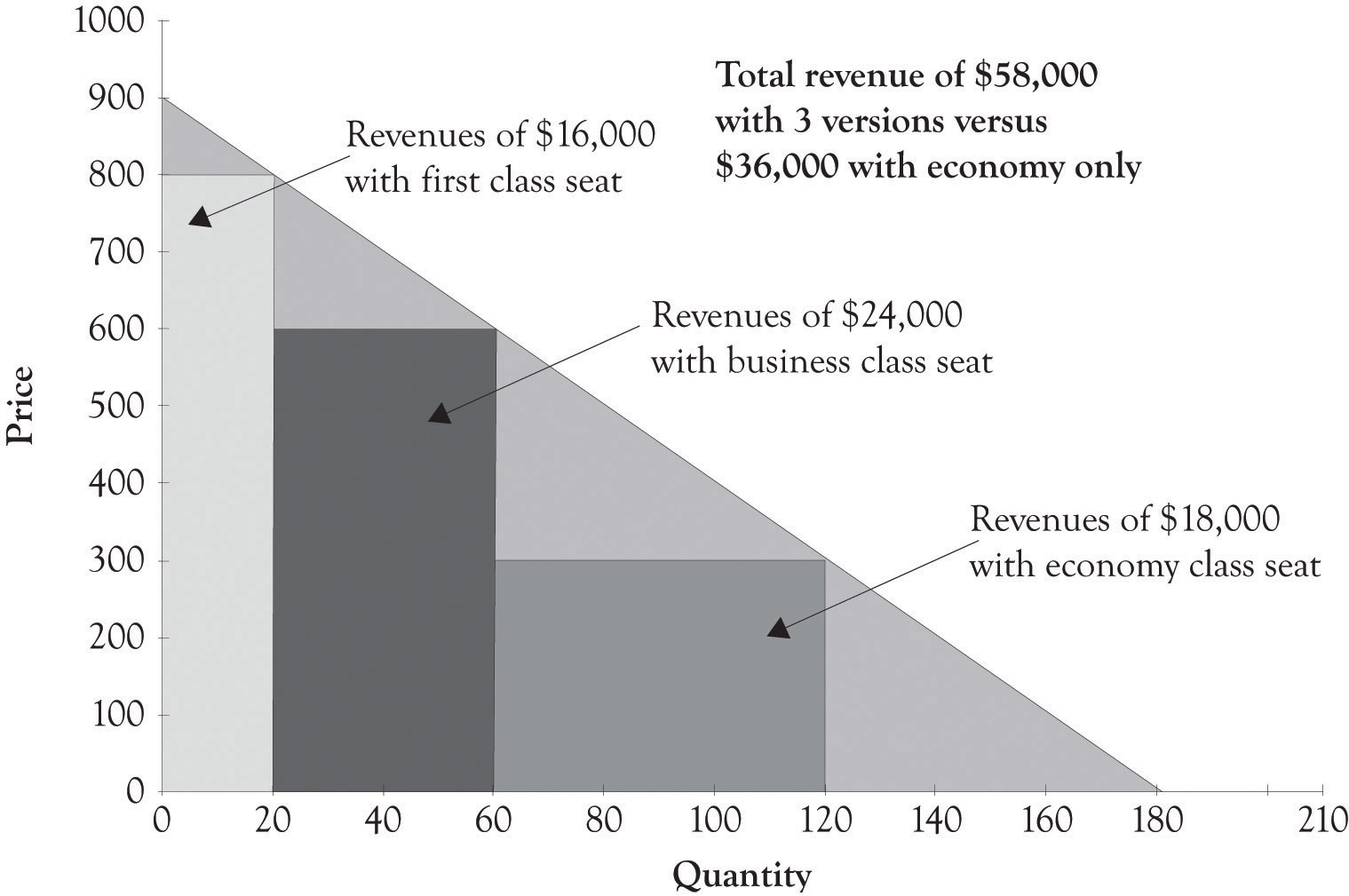
Second Degree Price Discrimination
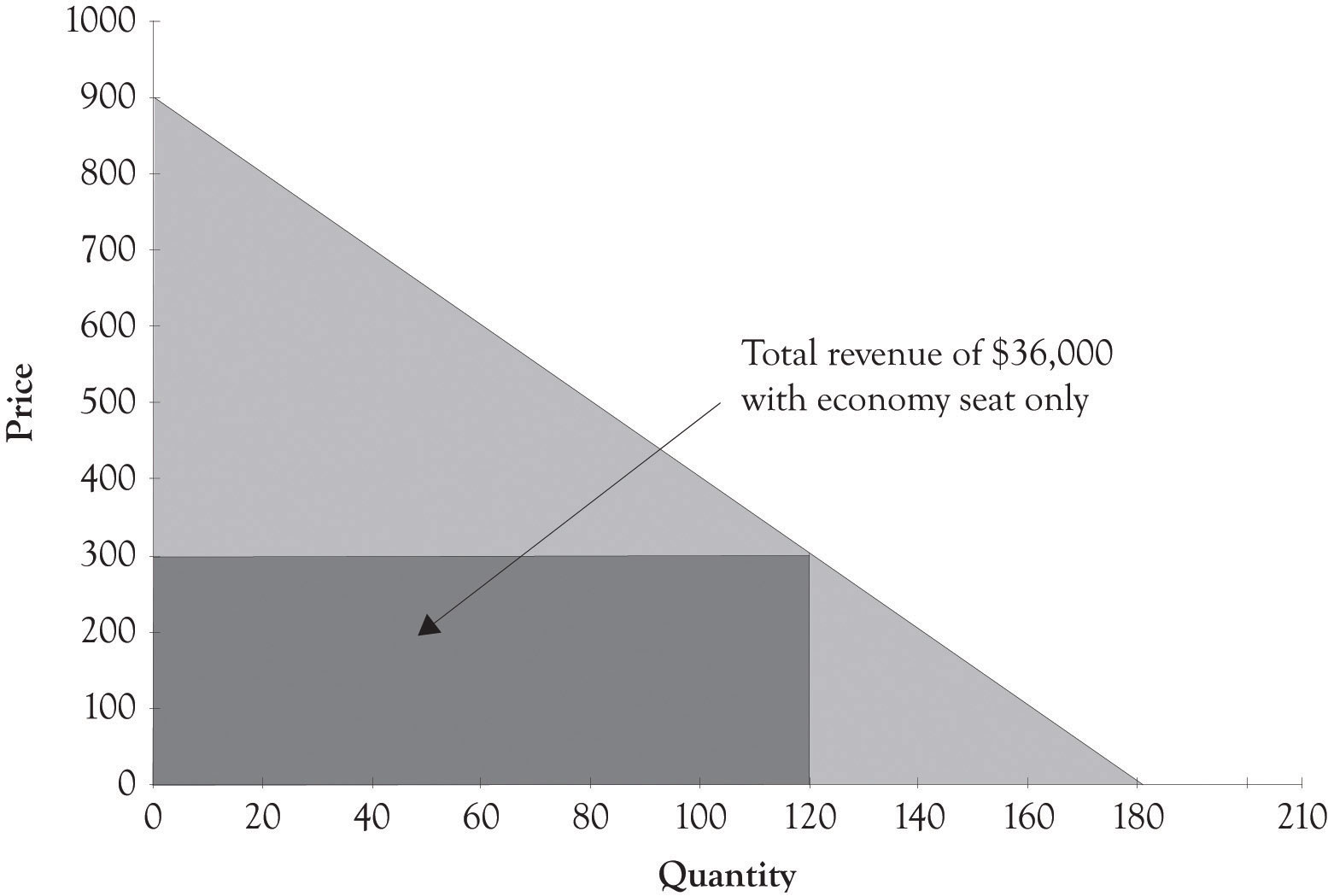
Second Degree Price Discrimination

Second Degree Price Discrimination
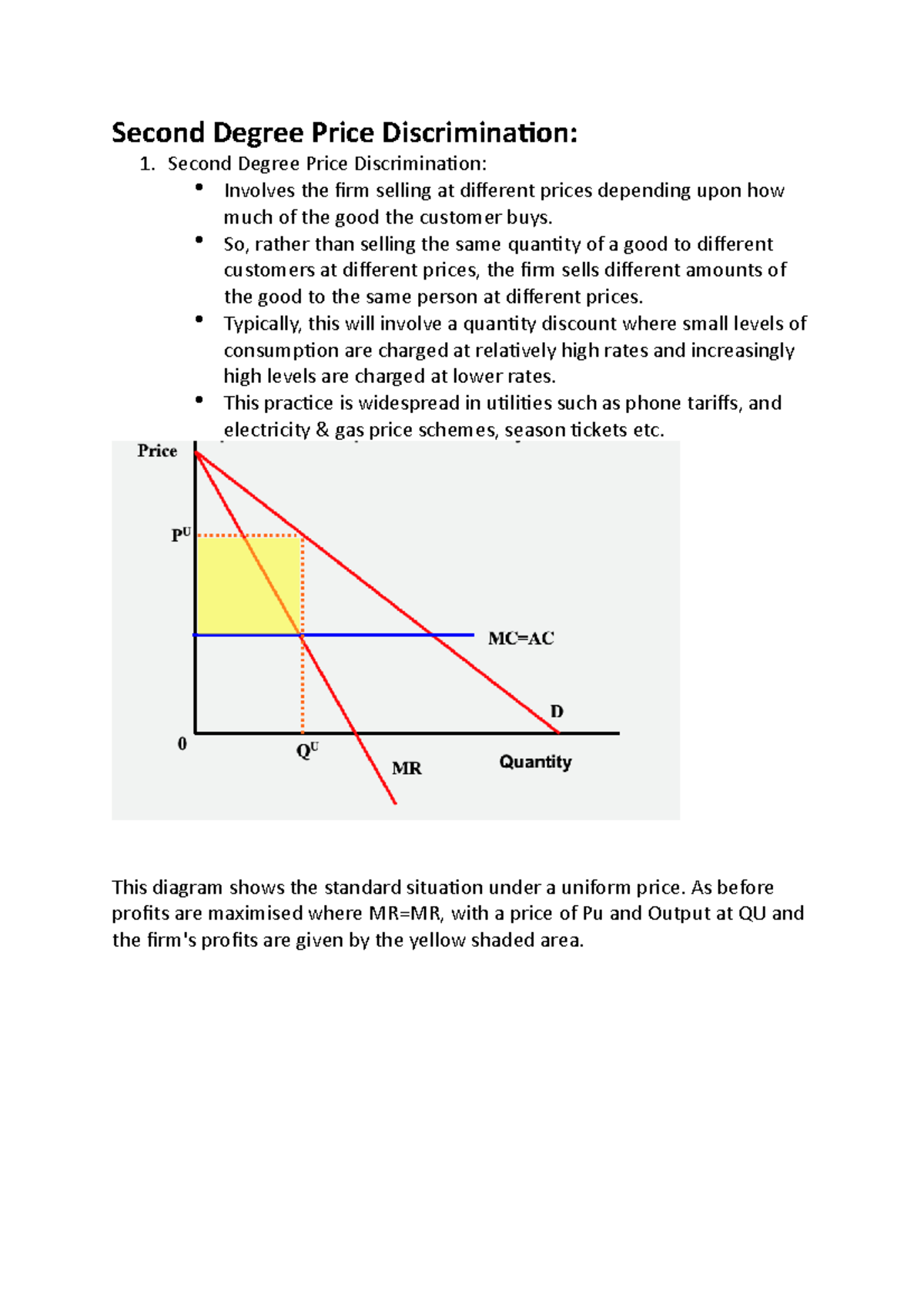
Second Degree Price Discrimination

Second Degree Price Discrimination

Second Degree Price Discrimination
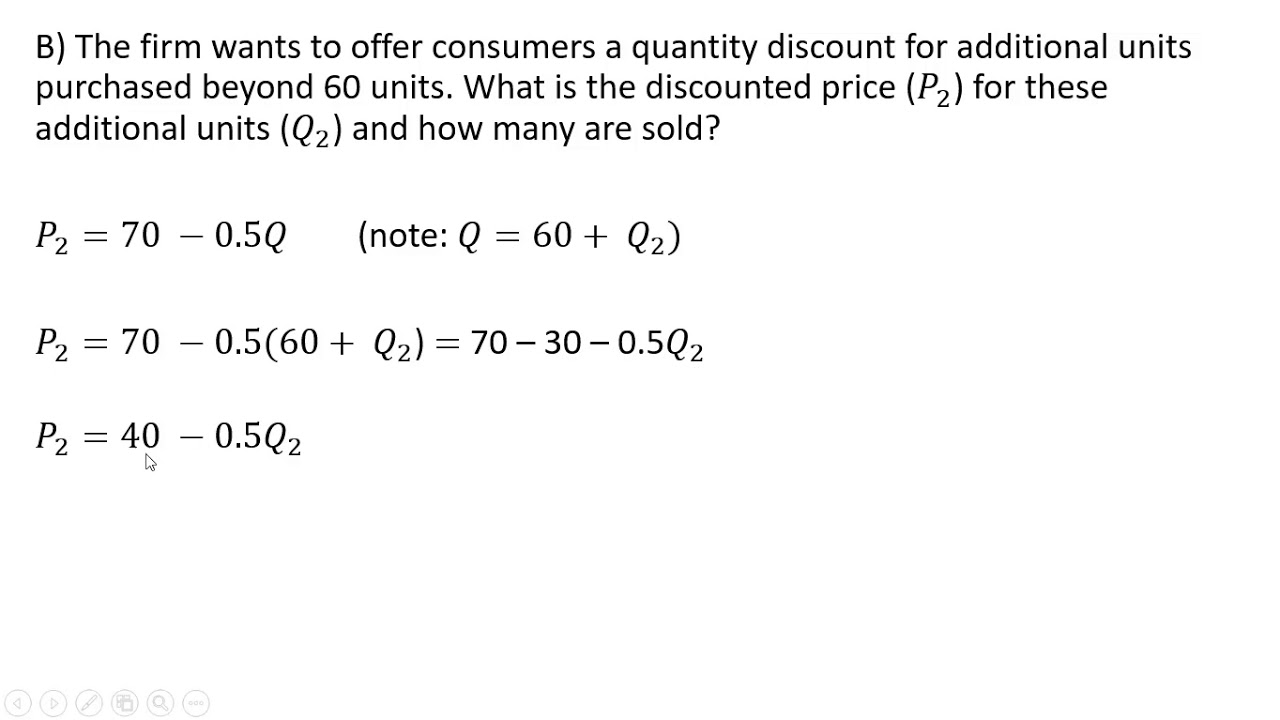
Second Degree Price Discrimination
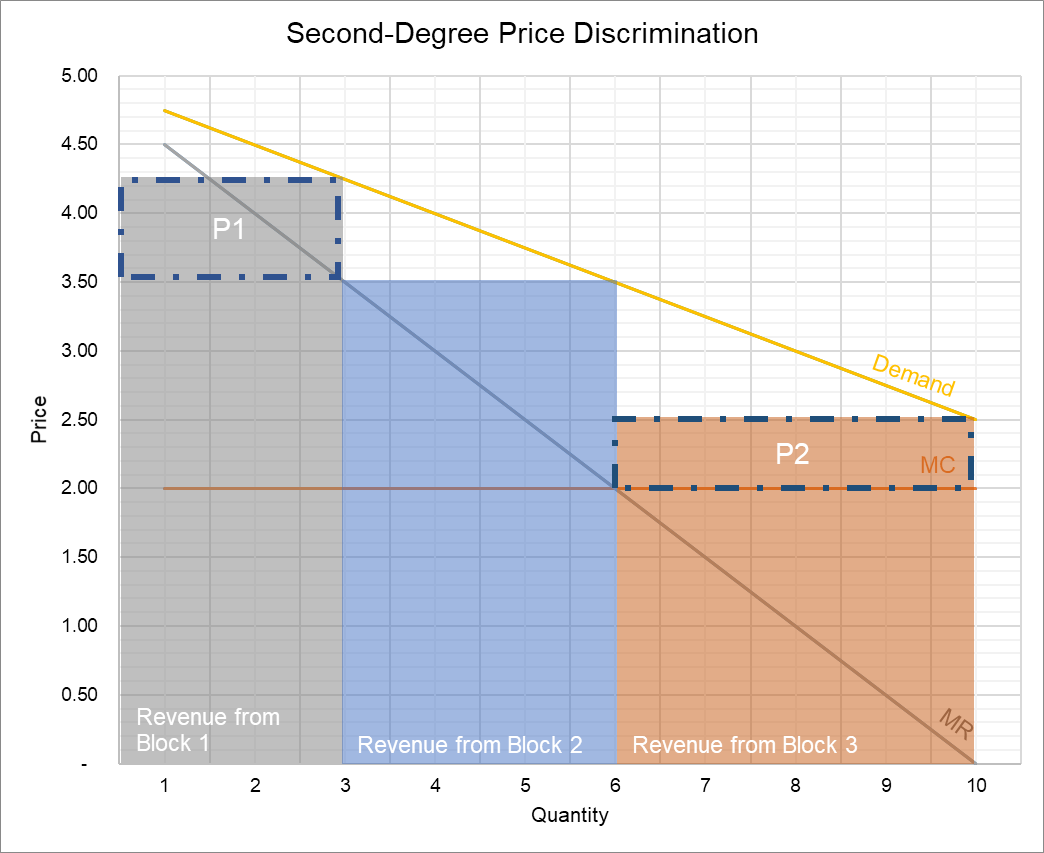
Second Degree Price Discrimination Graph And Example

Solved Second Degree Price Discrimination Solving This Chegg
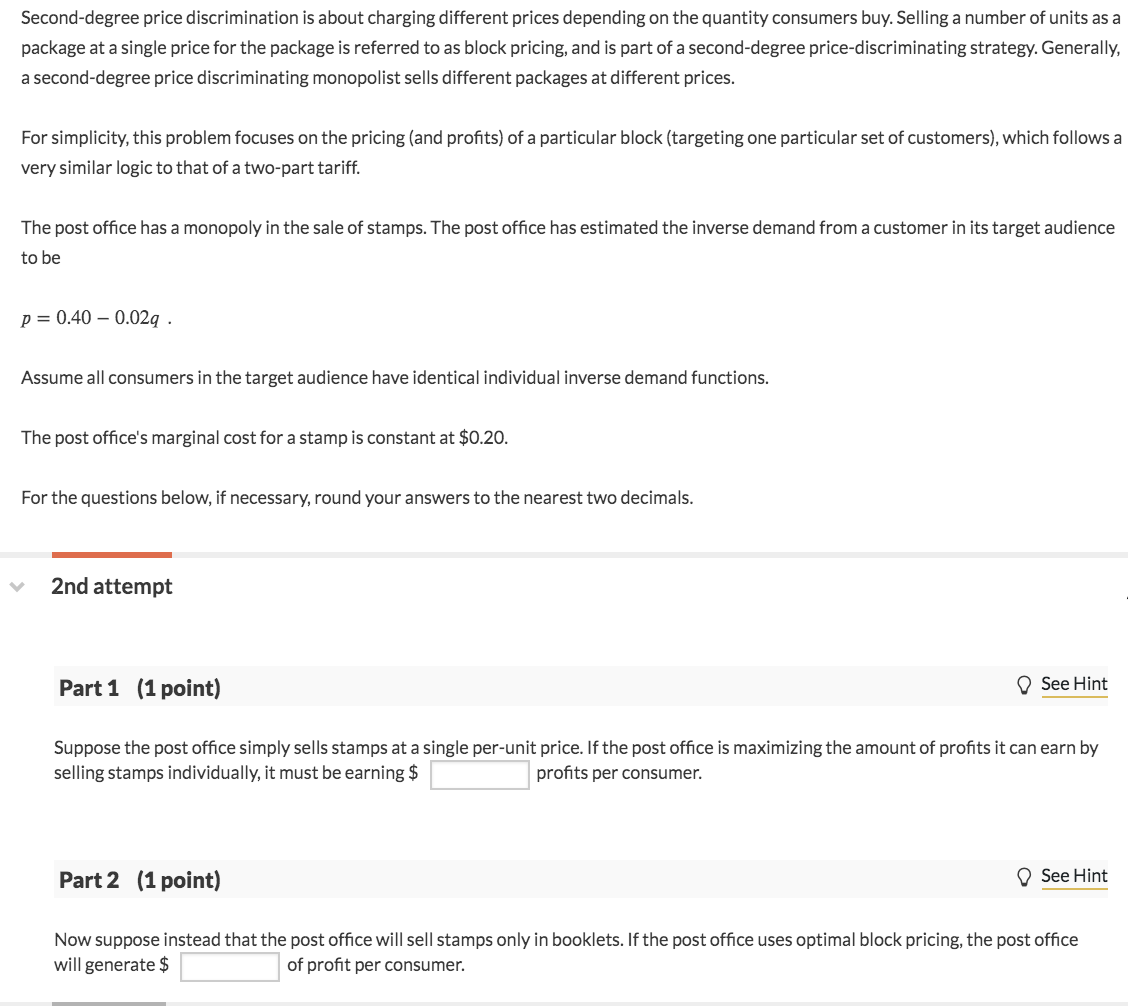
Solved Second degree Price Discrimination Is About Charging Chegg