What Is Molar Volume
What Is Molar Volume - Molar volume is the space occupied by one mole of a substance This term is used in chemistry to determine the molecular volume reflected in cubic meters per mol m 3 x mol 1 A mole is the unit contemplated by the International System of Units that allows to measure and express a certain amount of substance Molar volume Vmol sometimes noted only by V is the volume occupied by 1 mol of a compound or element at a given temperature and pressure The expression for Vmol is given by the formula 5 1 7 In expression 5 1 7 Mw is the molecular weight and is the density of the compound
What Is Molar Volume

What Is Molar Volume
Molar volume is the volume of one mole of a substance at a specified pressure and temperature. It is commonly denoted by the symbol V m . Units. The SI unit of molar volume is cubic meters per mole (m 3 /mol). However, because that is such a large volume, other units are usually used. Avogadro's Hypothesis and Molar Volume Volume is a third way to measure the amount of matter, after item count and mass. With liquids and solids, volume varies greatly depending on the density of the substance.
Molar Volume An Overview ScienceDirect Topics
/GettyImages-170037493-a7d9f8fbea8443cba6c664bbd741e9c4.jpg)
What Is Molar Volume Chemistry Definition
What Is Molar VolumeThe molar volume is the volume occupied by one mole of ideal gas at STP. Its value is: 22.414 L mol¯ 1. It is actually known to several more decimal places but the number above should prove sufficient.This value has been known for about 200 years and it is not a constant of nature like, say, the charge on the electron. In chemistry and related fields the molar volume symbol Vm 1 or of a substance is the ratio of the volume occupied by a substance to the amount of substance usually given at a given temperature and pressure It is equal to the molar mass
n, V m (1) The volume occupied by one mole of a substance. For an ideal gas, 22.4 Lmol –1. (2) The molar volume, symbol V m is the volume occupied by one mole of a substance (chemical element or chemical compound) at a given temperature and pressure. It is equal to the molar mass (M) divided by the mass density (ρ). Molar Volume Of Gases The Mole Concept YouTube Pin On Education
10 6 Avogadro s Hypothesis And Molar Volume

CHEMISTRY 101 Density Of A Gas Molar Volume And Molar Mass YouTube
Two properties are almost universally known; the molar volume of water at ambient pressure and 273.15 K 273.15 K is less than that of ice, and. the molar volume of water at 273.15 K 273.15 K decreases on heating to reach a TMD before increasing. Molar Volume Of Gases GCSE Lesson SC14e TRIPLE Teaching Resources
Two properties are almost universally known; the molar volume of water at ambient pressure and 273.15 K 273.15 K is less than that of ice, and. the molar volume of water at 273.15 K 273.15 K decreases on heating to reach a TMD before increasing. PPT Molar Volume PowerPoint Presentation Free Download ID 1459694 How To Calculate Molar Volume Of A Liquid
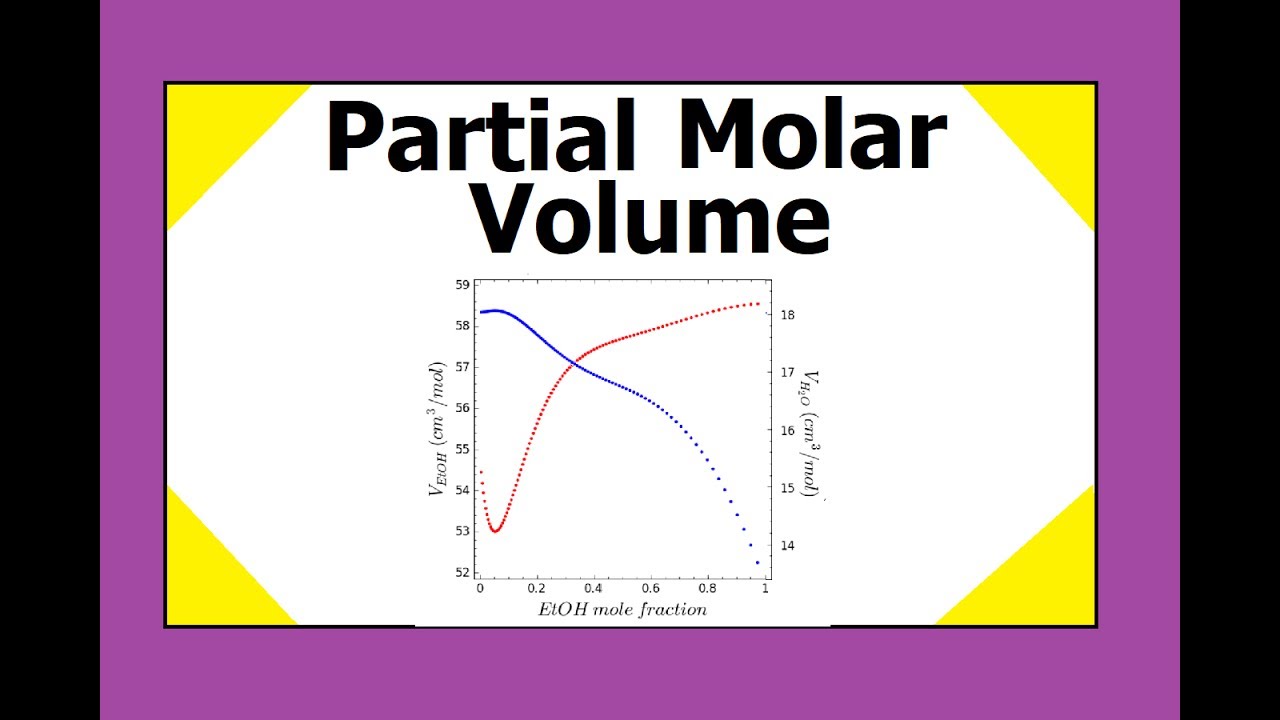
Partial Molar Volume YouTube

Molar Volume Calculated Two Different Ways YouTube
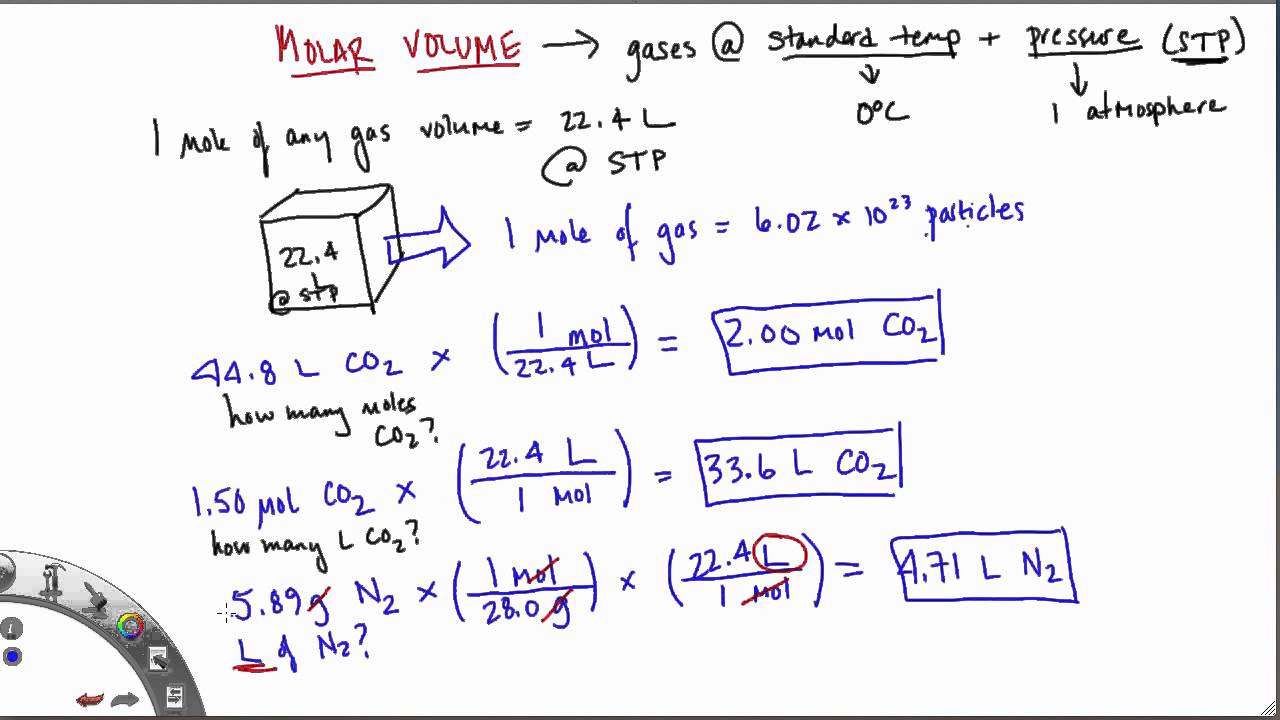
How To Calculate Partial Molar Volume
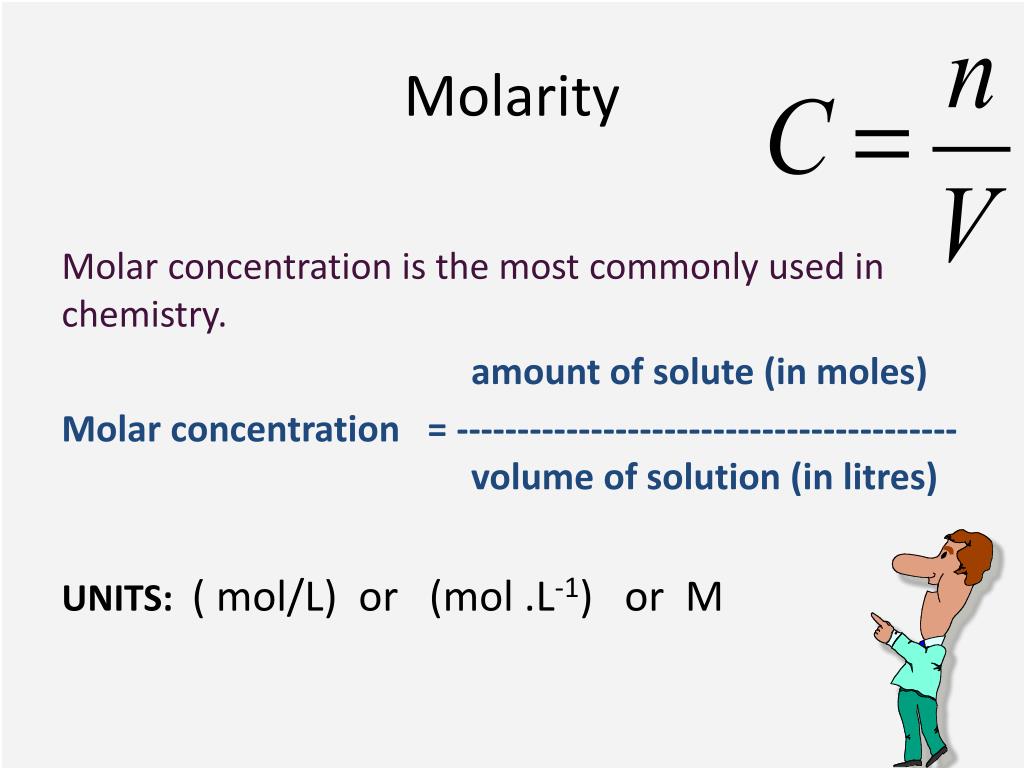
PPT Concentration PowerPoint Presentation Free Download ID 3874312
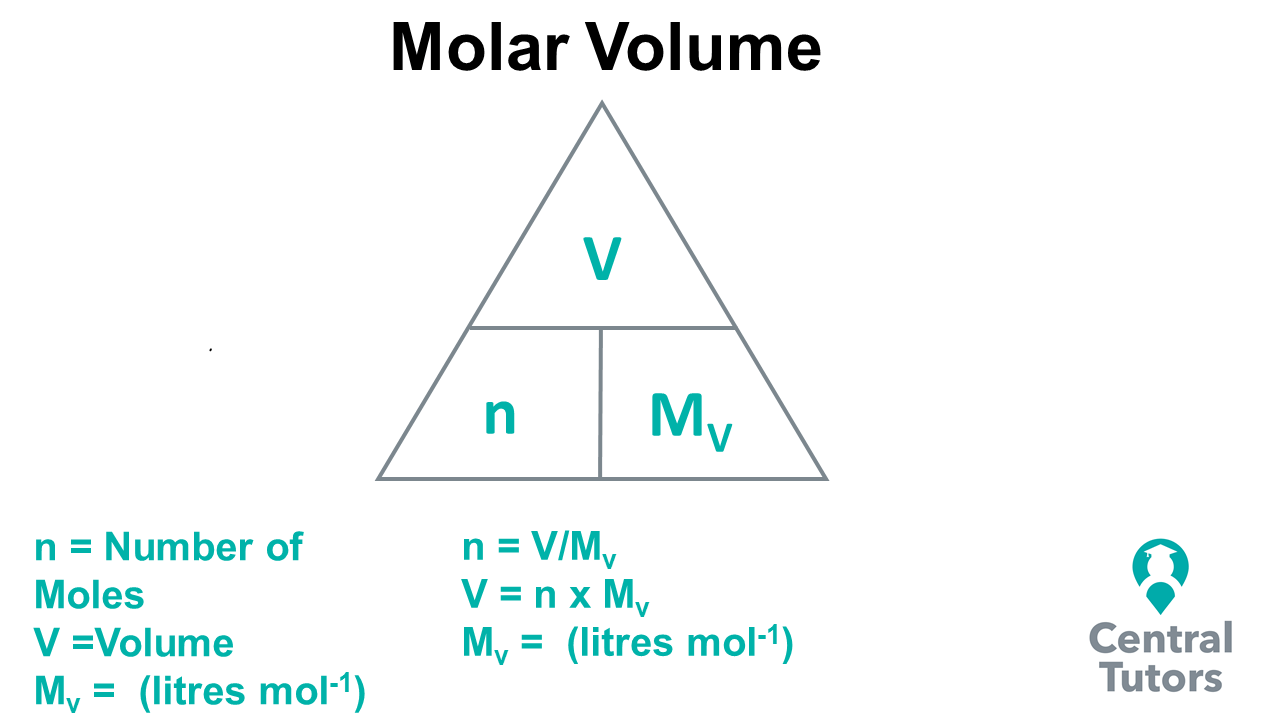
How To Solve Mole Calculations Using Molar Volume Central Tutors
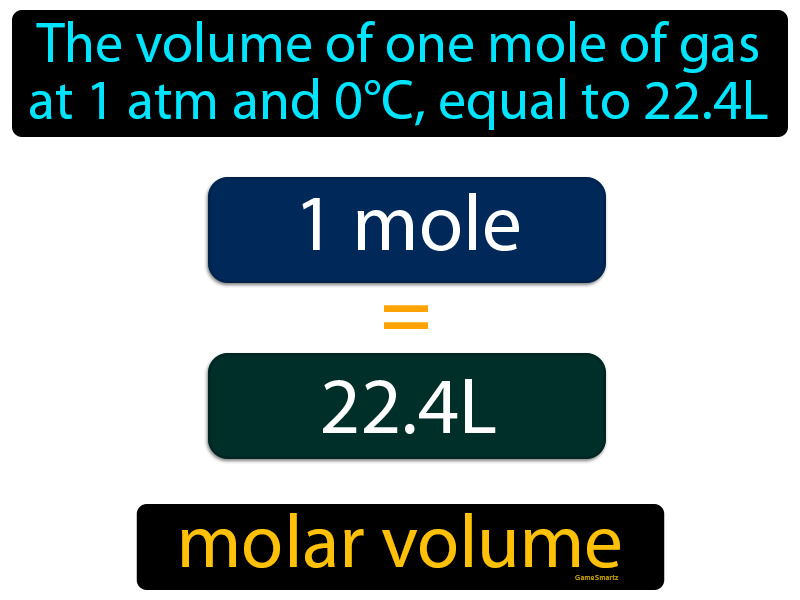
Molar Volume Definition Image GameSmartz

PPT Molar Volume Of A Gas PowerPoint Presentation Free Download ID

Molar Volume Of Gases GCSE Lesson SC14e TRIPLE Teaching Resources

Difference Between Molar Volume And Partial Molar Volume Definition

PPT Molar Volume PowerPoint Presentation Free Download ID 1459694