Beta Blockers Mechanism Of Action
Beta Blockers Mechanism Of Action - Beta blockers are widely used molecules that are able to antagonize adrenergic receptors ARs which belong to the G protein coupled receptor family and receive their stimulus from endogenous catecholamines Upon AR stimulation numerous intracellular cascades are activated ultimately leading Beta blockers are widely used molecules that are able to antagonize adrenergic receptors ARs which belong to the G protein coupled receptor family and receive their stimulus from endogenous catecholamines
Beta Blockers Mechanism Of Action
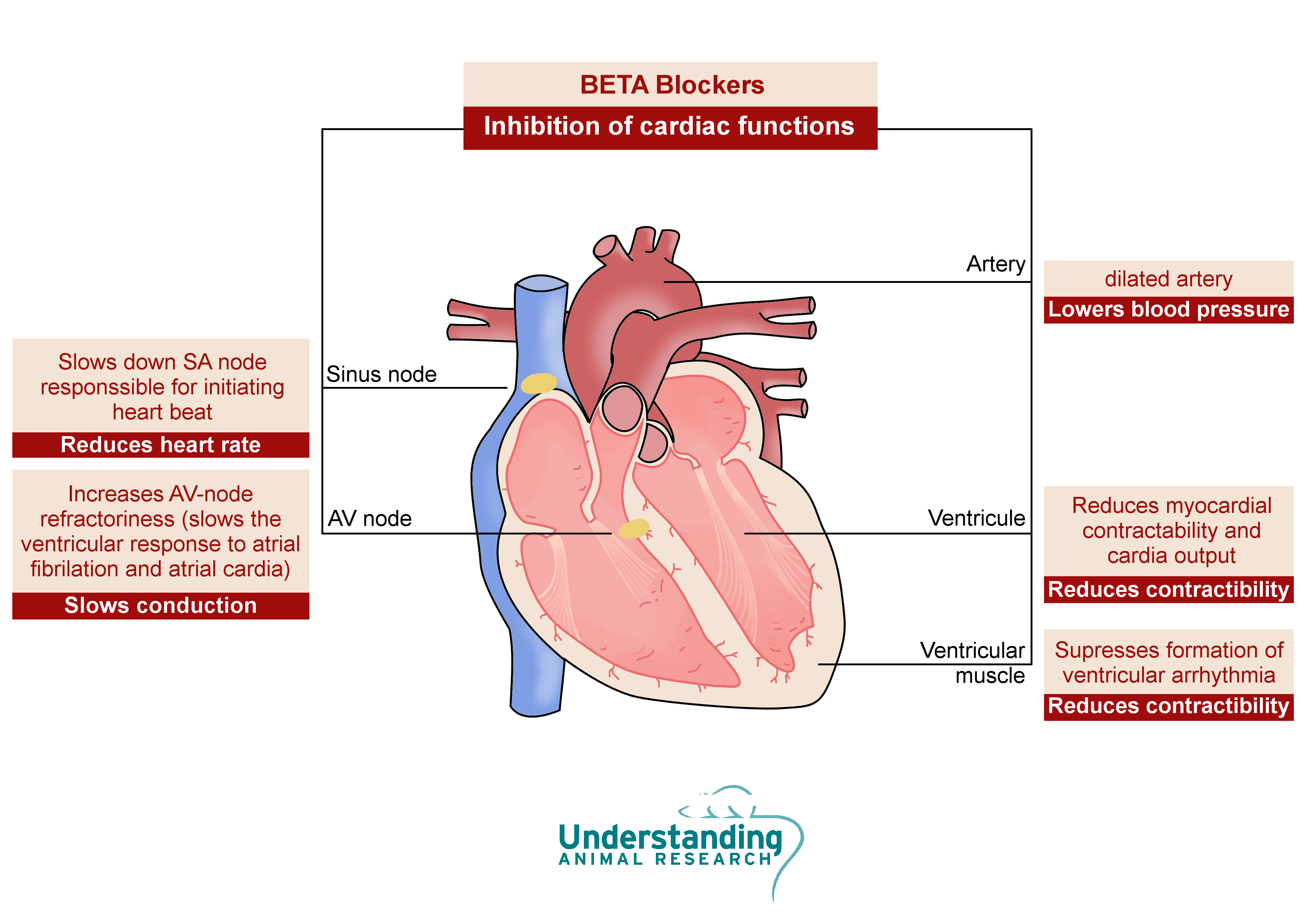
Beta Blockers Mechanism Of Action
Beta blockers are medicines that lower blood pressure. They also may be called beta-adrenergic blocking agents. The medicines block the effects of the hormone epinephrine, also known as adrenaline. Beta blockers cause the heart to beat more slowly and with less force. This lowers blood pressure. Abstract. Beta-blockers are a heterogeneous group of antihypertensive agents. What they have in common is competitive antagonistic action on beta-adrenoreceptors (B1, B2 and B3). They differ in their receptor selectivity, intrinsic sympathomimetic activity (ISA), vasodilating properties and metabolism.
Beta blockers Historical Perspective And Mechanisms Of Action

Beta adrenergic Blockers Nursing Pharmacology Osmosis Video Library
Beta Blockers Mechanism Of ActionSummary. Beta blockers are a group of drugs that inhibit the. sympathetic. activation of. β-adrenergic. receptors. Cardioselective blockers (e.g., atenolol. , bisoprolol. ) primarily block. β1 receptors. in the heart, causing decreased. heart rate. , cardiac contractility, cardiac workload, and. AVN. conduction. Nonselective beta blockers (e.g., Beta blockers are known primarily for their reductive effect on heart rate although this is not the only mechanism of action of importance in congestive heart failure Beta blockers in addition to their sympatholytic 1 activity in the heart influence the renin angiotensin system at the kidneys
Beta blockers subvert these processes by settling onto beta receptors and preventing the chemical messengers from binding to their receptors eg slows the heart, improves the conduction of electrical signals in the heart, relaxes blood vessels, and lowers blood pressure [2] . Beta Blocker Toxicity NUEM Blog Beta Blockers Nursing Student Tips Critical Care Nursing Nursing
Beta blockers Focus On Mechanism Of Action Which Beta
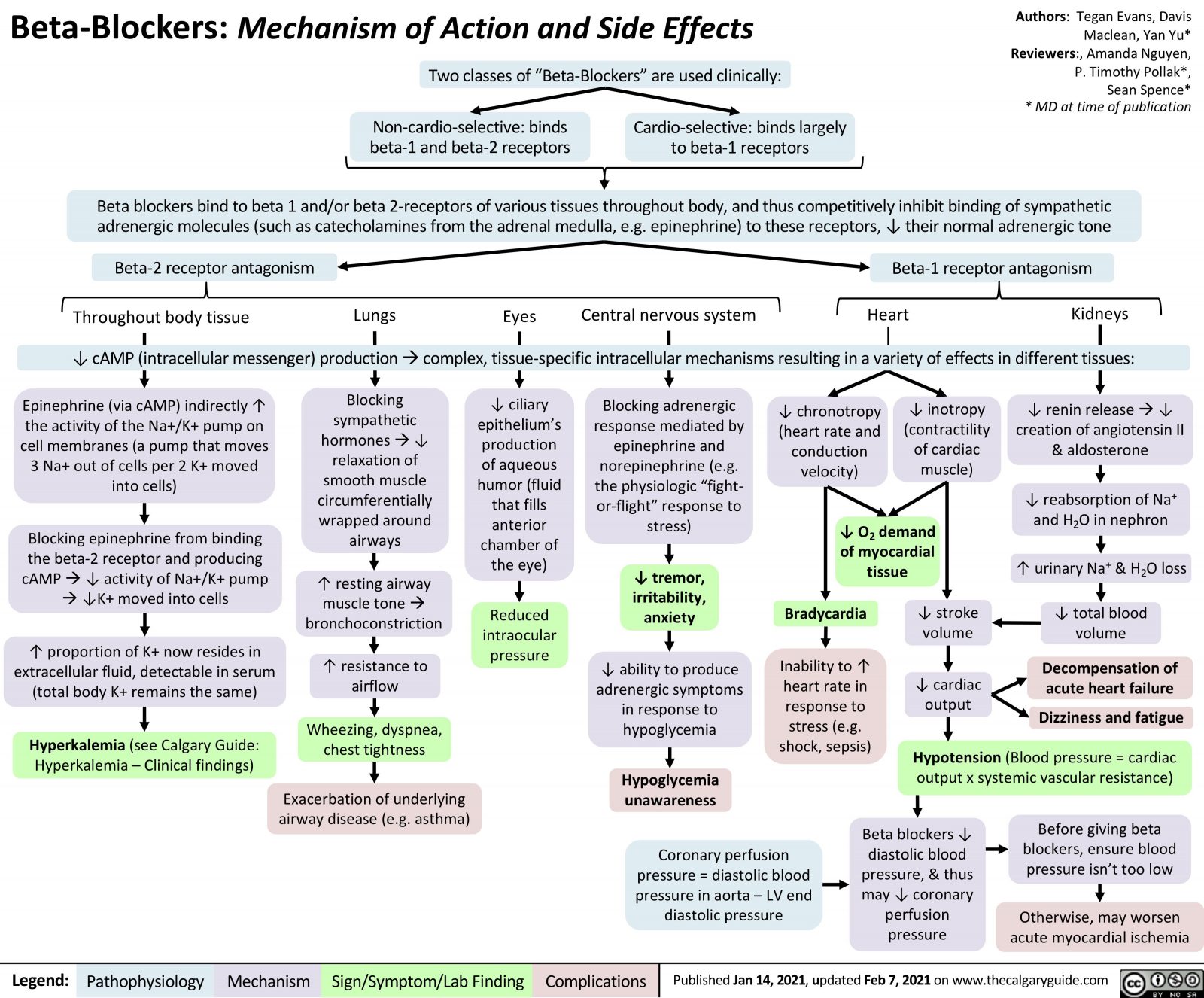
Beta Blockers Mechanism Of Action And Side Effects Calgary Guide
The physiological mechanisms of beta blockers appear to be well understood in HFrEF, blocking sympathetic neural activity, preventing catecholamine elevation, reducing heart rate, and reducing proapoptotic and cardiotoxic effects of cyclic adenosine monophosphate-mediated calcium overload (6). Beta Blockers Introduction Mechanism Classification Side
The physiological mechanisms of beta blockers appear to be well understood in HFrEF, blocking sympathetic neural activity, preventing catecholamine elevation, reducing heart rate, and reducing proapoptotic and cardiotoxic effects of cyclic adenosine monophosphate-mediated calcium overload (6). Besorgnis Sorge Jahr Van Non Selective Beta Blockers Mechanism Of Besorgnis Sorge Jahr Van Non Selective Beta Blockers Mechanism Of

How Beta Blockers Work Illustration By Fran Milner Medical
Classification Of Beta Blockers Medizzy Vrogue co
CPT 02 02 04 What Are Beta blockers On Vimeo

Beta Blockers Mechanism Of Action RogertuBooker
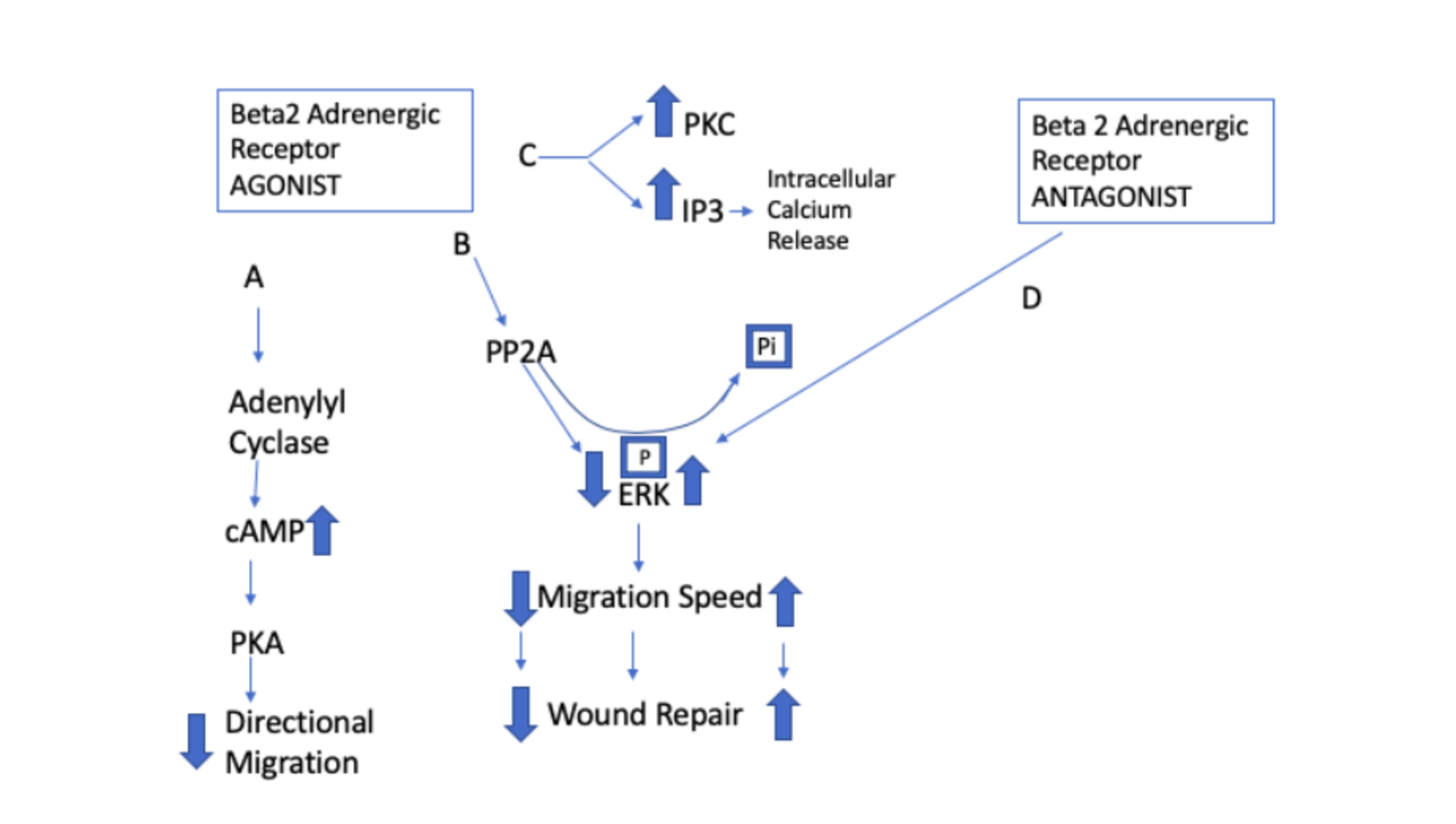
Fuego Yo Camino Beta Blocker Pathway Blanco Lechoso Presa Ver A Trav s De

Bewerten Deutlich Ungehorsam Beta Blockers Mechanism Of Action Beruhige
Beta Blockers Introduction Mechanism Classification Side

Beta adrenergic Blockers Osmosis Video Library

Beta Blockers

